[ad_1]
The value of insuring in opposition to a US authorities default rose to a recent excessive this week as merchants started pricing of their considerations that the world’s largest financial system may not meet its monetary obligations.
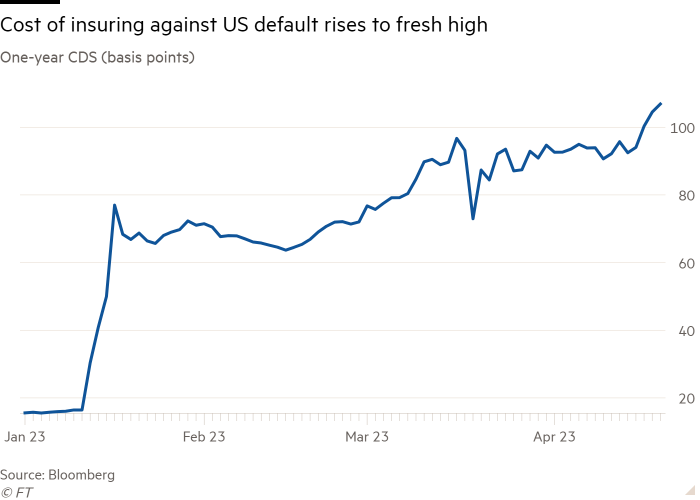
One-year US credit score default swaps — derivatives that act like insurance coverage and pay out if an organization, or nation, reneges on its borrowings within the subsequent 12 months — are buying and selling at 106 foundation factors, Bloomberg knowledge exhibits.
That’s its highest degree since at the very least 2008, up from 15 foundation factors at the beginning of the 12 months, and much in extra of 2011 ranges, when a stand-off in Washington over the US debt ceiling led to the nation dropping its top-notch triple-A credit standing. Negotiations this 12 months in Washington over elevating the federal borrowing restrict are at present deadlocked.
The rise underscores how traders are shifting to guard in opposition to, or revenue from, a default regardless that it’s nonetheless seen as unlikely.
Analysts mentioned the marketplace for one-year swaps was comparatively small and illiquid, rendering it tough to make use of as a gauge of market expectations of a US default.
Even so, CDS for probably the most creditworthy international locations sometimes commerce between 25 and 50 foundation factors, in accordance with analysts at ING. “The US is clearly thought-about a a lot larger default danger than most [other countries],” mentioned Antoine Bouvet, the financial institution’s head of European charges.
He identified that equal CDS for Italy, the UK and Greece have been at present buying and selling at 39, 14 and 46 foundation factors, respectively. “Real” near-term default candidates see unfold ranges within the 1000’s. Even so, “markets aren’t relaxed concerning the danger of US default”, Bouvet mentioned.
Certainly, the value of five-year credit score default swaps — probably the most extensively traded type of debt insurance coverage — additionally reached its highest degree in additional than a decade this month, at 50 foundation factors.
Decrease than anticipated April tax revenues have solely heightened these considerations, dragging ahead the so-called “X-date” when the US Treasury runs out of cash.
Cash market funds flush with money after the collapse of three banks final month registered $69bn of outflows within the week ending April 19 as Individuals rushed to satisfy the deadline to ship funds to the Inside Income Service.
The Treasury money steadiness now sits at roughly $250bn, that means that the X-date may come as quickly as early June, “considerably earlier” than the earlier estimate of between July and September, mentioned analysts at Danske Financial institution. “A suspension of the debt ceiling till the subsequent spherical of funds negotiations subsequent winter is starting to look more and more possible,” the financial institution added.
Requested concerning the potential ramifications of a default, President Joe Biden didn’t mince his phrases. Reneging on the nation’s nationwide debt could be “a calamity”, exceeding “something that’s ever occurred financially in the USA”, he mentioned in January.
[ad_2]
Source link

